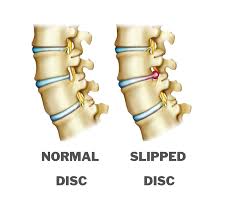
Causes of Slip Disc
Several factors contribute to the development of a slip disc:
- Age: As we age, the discs in our spine lose water content and elasticity, making them more prone to herniation.
- Injury: Trauma or injury to the spine, often from lifting heavy objects or sudden movements, can cause a disc to slip out of place.
- Genetics: Some people may have a genetic predisposition to developing slip discs due to inherited traits affecting the structure of their spinal discs.
- Lifestyle: Sedentary lifestyles, coupled with poor posture and lack of exercise, can weaken the muscles that support the spine and contribute to disc herniation.
- Occupational Factors: Jobs that involve heavy lifting, repetitive movements, or prolonged sitting can increase the risk of developing spinal problems, including slip discs.
Symptoms of Slip Disc
The symptoms of a slip disc can vary depending on the location and severity of the herniation. Common symptoms include:
- Pain: This is the most prevalent symptom and can range from mild to severe. The pain may be localized in the affected area or radiate to other parts of the body, such as the legs or arms, depending on where the herniation occurs.
- Numbness and Tingling: Pressure on the nerves from a slip disc can cause numbness, tingling sensations, or weakness in the muscles served by those nerves.
- Changes in Reflexes: In some cases, a slip disc can affect reflexes, leading to changes in how muscles respond to stimuli.
- Difficulty Moving: Stiffness and difficulty in bending or twisting the spine may occur, especially if the slip disc causes muscle spasms or inflammation.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosing a slip disc typically involves a combination of physical examination, medical history review, and diagnostic imaging tests. Such as X-rays, MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging), or CT (Computed Tomography) scans. Once diagnosed, treatment options vary depending on the severity of symptoms:
- Conservative Treatment: For mild to moderate cases, conservative treatments may be recommended, including:
- Rest: Avoiding activities that aggravate symptoms.
- Pain Management: Over-the-counter or prescription medications to relieve pain and inflammation.
- Physical Therapy: Exercises and stretches to strengthen the muscles supporting the spine and improve flexibility.
- Heat or Ice Packs: Applying heat or ice packs to the affected area to reduce inflammation and ease pain.
- Interventional Treatments: If conservative treatments do not provide relief, or if the symptoms are severe, more invasive treatments may be considered, such as:
- Epidural Steroid Injections: Injecting corticosteroids into the space around the spinal cord to reduce inflammation and relieve pain.
- Manual Manipulation: Chiropractic adjustments or osteopathic manipulation to help realign the spine and reduce pressure on the affected disc.
- Surgical Options: If other treatments fail to relieve symptoms or if nerve compression persists, surgery may be necessary. Surgical procedures for slip discs include:
- Discectomy: Removal of the herniated portion of the disc to relieve pressure on the nerves.
- Laminectomy: Removal of a portion of the vertebral bone (lamina) to create more space and reduce pressure on the spinal cord or nerves.
Lifestyle Modifications and Prevention
Preventing slip discs and maintaining spinal health involves adopting healthy habits and making lifestyle changes:
- Exercise Regularly: Strengthening the muscles that support the spine through regular exercise can help reduce the risk of disc herniation.
- Practice Good Posture: Maintaining proper posture while sitting, standing, and lifting can reduce strain on the spine.
- Avoid Smoking: Smoking can impair the blood supply to spinal discs, accelerating degeneration and increasing the risk of herniation.
- Use Proper Lifting Techniques: When lifting heavy objects, bend at the knees and keep the object close to your body to reduce strain on the spine.
- Take Breaks: If your job involves prolonged sitting or repetitive movements, take breaks to stretch and change positions.
Conclusion
A slip disc is a common spinal condition that can cause significant pain and discomfort, affecting daily activities and quality of life. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for slip discs is crucial for early diagnosis and effective management. By adopting healthy habits, practicing good posture, and seeking prompt medical attention for symptoms. Individuals can reduce slip disc risks and maintain optimal spinal health. If you suspect a slip disc or experience symptoms, consult a healthcare professional for evaluation and treatment advice.
